Introduction to Bond Investments
Investing in bonds is one of the safest and most reliable methods to secure steady returns over time. In India, bonds serve as a popular investment choice for individuals looking to diversify their portfolios or for those who seek lower-risk alternatives compared to equities. This guide will provide a detailed look into bond investments in India, including types, benefits, potential returns, and essential calculation methodologies.
What Are Bonds?
Bonds are debt instruments issued by corporations, financial institutions, or the government to raise funds. When you invest in bonds, you’re effectively lending money to the issuer in return for periodic interest payments. At the end of the bond term, the principal amount is returned to you. Bonds can vary in terms of interest rates, durations, and risk levels.
Types of Bonds Available in India
- Government Bonds: Issued by the Government of India and considered one of the safest investments.
- Corporate Bonds: Issued by companies; these offer higher interest rates but come with slightly higher risks.
- Tax-Free Bonds: These bonds offer interest payments that are exempt from income tax, making them attractive to high-net-worth individuals.
- Municipal Bonds: Issued by local government bodies for infrastructure projects, providing lower risks and decent returns.
- Sovereign Gold Bonds (SGBs): Bonds backed by gold, issued by the RBI on behalf of the Government of India.
Benefits of Bond Investments in India
- Stable Returns: Bonds offer fixed interest rates, ensuring stable returns.
- Capital Preservation: Bonds generally have lower risks than stocks, making them suitable for conservative investors.
- Tax Benefits: Some bonds offer tax exemptions on interest income.
- Portfolio Diversification: Bonds help balance the risk of high-volatility assets in your portfolio.
How to Analyze Bond Investments
When considering bond investments, investors should evaluate the following key factors:
1. Interest Rate (Coupon Rate)
The interest rate, or coupon rate, is the return on your bond investment. For example, a bond with a 6% coupon rate on a ₹10,000 face value will pay ₹600 annually. Always compare the coupon rate with prevailing interest rates to determine if it’s competitive.
2. Yield to Maturity (YTM)
YTM is a key metric used to calculate the total return an investor can expect if the bond is held until maturity. YTM factors in the bond’s current market price, face value, interest rate, and time remaining to maturity. Here’s the formula
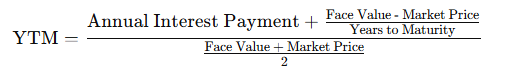
3. Duration and Maturity
- Duration reflects the bond’s sensitivity to interest rate changes. Longer durations mean greater interest rate risk.
- Maturity refers to the bond’s end date, when the principal is returned. Bonds with longer maturities often offer higher interest rates but come with increased risks.
4. Credit Rating
Credit rating agencies like CRISIL, ICRA, and CARE assess the creditworthiness of bonds. Bonds with higher credit ratings (e.g., AAA) indicate lower risk of default, making them safer but potentially offering lower returns.
Calculation Methodology for Bond Analysis
Example: Calculating Yield to Maturity (YTM)
Let’s consider a bond with:
- Face Value = ₹1,000
- Market Price = ₹950
- Coupon Rate = 7%
- Years to Maturity = 5
- Annual Interest Payment = Face Value × Coupon Rate = ₹1,000 × 0.07 = ₹70
- YTM Calculation:
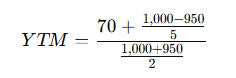
Solving this gives the YTM as approximately 7.58%. This means if you buy this bond at ₹950 and hold it to maturity, your expected yield will be about 7.58% per year.
Where to Invest in Bonds in India
Investors can buy bonds through:
- Stock Exchanges: Bonds can be purchased through NSE or BSE using a demat account.
- Brokers: Some brokers specialize in bond investments and offer personalized bond portfolios.
- RBI Retail Direct Scheme: Investors can directly invest in government bonds through the RBI’s Retail Direct platform.
- Mutual Funds: Bond mutual funds offer exposure to diversified bond portfolios.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Bond Investments
Advantages:
- Lower volatility compared to equities
- Fixed income and capital protection
- Tax benefits with specific types of bonds
Disadvantages:
- Lower returns compared to high-growth assets
- Interest rate risk, especially for long-term bonds
- Potential for lower liquidity compared to stocks
Conclusion
Bond investments in India provide a stable and reliable option for conservative investors, offering a good balance between safety and returns. By understanding key metrics like YTM, duration, and credit ratings, investors can make informed decisions that align with their risk tolerance and financial goals.


